The Ultimate KPI Guide

What does KPI mean?
KPI stands for 'Key Performance Indictor'.
What is a KPI?
A KPI is a performance measure (someties refered to as a 'metric') quantifying something that we care about or is important in some way. Head here for a 60 second explanation of KPIs using kittens.
What is the difference between a KPI, PI, metric and performance measure?
Metric, measure and indicator are three different ways of describing the same thing, 'something we measure'.
Deciding whether a Performance Indicator is, or is not, a KPI creates huge amounts of debate and strong opinions. This debate will never be settled because the importance of a measure depends on the situation it is being used in, so there can never be a definitive list of 'what is a PI and what is a KPI'.
How do we separate KPIs from PIs?
With no centralised list of what makes a measure 'Key' or not, it comes down to which measures are important to us, our organisation or our specific situation. We must rank our measures relative to each other, with the highest ranking measures earning the title 'KPI'. This can be managed formally using the 'Shortlisting' step from the ROKS method.

The seven principles of good KPI design and definition
Before we dive into the best method for choosing and defining our KPIs let's take a look at the principles those methods are based on...
That sounds like a lot to remember
If this all seems a bit overwhelming, don't worry. We have not one, but two KPI definition methods you can use that are built around these principles. Here's why we need two methods...
The nature and complexity of your organisation has a big impact on the way in which you choose your KPIs. Here's a quick guide to help you choose the right approach...
Still not sure which approach to use?
The ROKS Express method has been built using the tools of the ROKS Enterprise method, so if you aren't sure, start with the ROKS Express approach, you can always extend it later with the Enterprise approach.
How to define KPIs for smaller businesses

ROKS Express:. The perfect solution for small-medium sized commercial organisations looking to kickstart their growth. Using a simple questionnaire, this system will help you get up and running with your core KPIs in hours, not weeks.
Show me the ROKS Express method!
ROKS Express KPI definition process overview
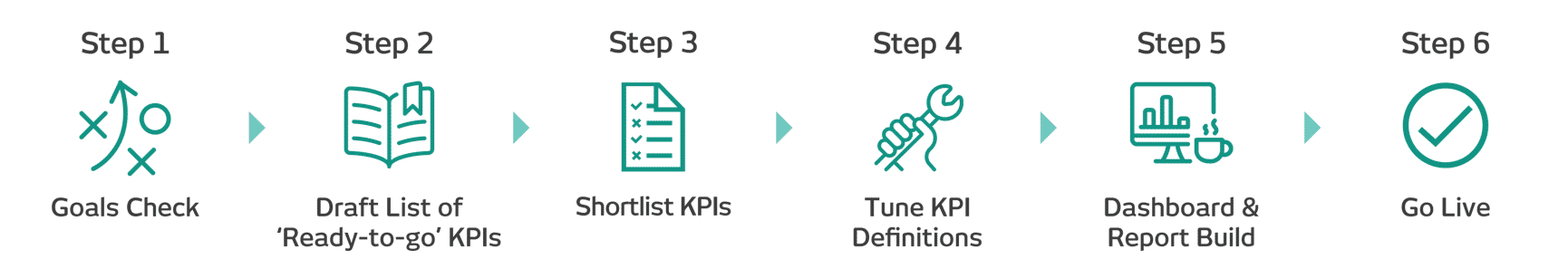
ROKS Express: Each step in detail
Step 1: Goals check
Knowing what you want to achieve is THE critical foundation of any well designed KPI set. Think of it as 'deciding what DIY task you want to complete before you go to the DIY superstore'. You would have a much better idea of which tools and materials to buy if you put some thought in at the start.
- Think hard about what you want from your business and from life.
- Create your ‘First-Draft Objectives’ and identify your ‘Key Results’.
- State what result achieving each of the objectives will deliver and record as an ‘Objective Key Result’ - OKR.
- Double-check that your objectives and high-level targets are ready-to-go using the ‘Pre-flight objectives checklist’.
Step 2: Draft the 'Ready to go' list of KPIs
Many businesses share common characteristics. We call these 'traits' and combined they can rapidly build up a full description of the families of KPIs we need for our business. Here is a sample of some of these 'traits'...
- Staff and payroll
- Equipment investment
- Footfall
- Sensitive customer data stored
- Sales value, activity and results
- Stock
There are 52 traits in total, which when combined, can describe the vast majority of 'normal' organisations. Larger or mission-focussed organisations may not have full coverage from these traits (they need the ROKS Enterprise method)
In this step we...
- Identify the ‘business traits’ that apply to your business, using a simple survey tool.
- Use the survey to select the KPI Families you need to review.
- Here are some sample definitions to get you started...
- Review the relevant KPI Families to select your KPI Longlist, ready for trimming down to the essentials in Step 3.
All 413 pre-defined KPIs, with worked examples, are included in...
Step 2 is a great way to come up with a draft list of KPIs, but the list will be far too long. The next stage is to take that list of KPIs and cut it down to a much shorter list that will be practical to implement. We do this using 'Sifting questions' followed by a scoring process called 'Shortlisting'.
Step 3: Shortlist KPIs
Rapidly reduce the KPI Longlist by asking the ‘Sifting questions’.
- Use the KPI Shortlisting Template to score each candidate KPI for Importance and Ease of Measurement.
- Shortlist your KPIs by scoring rank, deciding on your cut-off threshold and any exceptions that you may want to make.
Step 4: Tune KPI definitions
Once we have a shortlist of KPIs, we need to make sure these KPIs are clearly 'explained' using a structured definition template and we need to decide on targets for those KPIs.
Why do we need KPI definitions?
Human language is designed to tell stories. It does this through a rich selection of words. Many of these words overlap. Sometimes the same word can paint completely different pictures in people’s minds.
The human mind also has a fantastic ability to fill in gaps and blanks using our imagination. This ability is one reason so many people prefer the written version of a story over the film; their minds seamlessly fill in the missing details.
Now if you are a novelist, this effect is fantastic. A few well-chosen words can set off a fireworks display of imagination in the reader. If you are trying to measure something, it’s a potential disaster. We need to be precise and clear in how to calculate a metric or KPI.
Here's what we need to do...
- Clearly and simply tailor the definitions of the Shortlisted KPIs to your specific organisation and record other useful information, such as where the data is stored, what the known problems with the KPI are and who the owners of the KPI and definition are.
- You may also decide to create KPI Cheat Sheets, as a training aid or support tool for your team.
- Think carefully about the targets you set, the behaviours they might drive and whether you can make your targets more engaging.
- Reach agreement with those the targets will affect.
Step 5: Dashboard and report build
Now that you have designed your individual KPIs you need some way of presenting them for review and decision-making. The normal way of presenting KPIs is using a dashboard (quick summary overview of the situation) or through reports (normally a more in-depth view of a situation).
Dashboards and reports come in all sorts of styles and complexities. They range from a simple print-out of some figures on a spreadsheet through to sophisticated ‘infographics’.
In the dashboard and report build step you...
- Decide how and when you will review your KPIs
- Decide how you will present and review your KPIs
- Understand the simple rules of clear report and dashboard design
- Its also recommended that you learn some tips and tricks for designing and customising Excel reports and dashboards if you are using Excel
Designing clear easy-to-read dashboards and reports should not be guesswork. There are clear principles of visual design, which will make dashboards quick and intuitive to understand if you follow them, or cluttered and confusing you break them. These rules are based on careful academic research by the likes of Edward Tufte, Stephen Few and many others.
Step 6: Go live
All your hard work so far will be for nothing, if you don't roll out your new KPIs, reports and dashboards. Roll-out doesn't just include developing a plan, we also need to think about the practicalities and problems we are likely to face. It's crucial to...
- Plan your KPI rollout carefully
- Start collecting data
- Put your KPIs into action
- Deal with the inevitable hiccups and implementation problems
Why you need a KPI implementation plan
KPIs are like New Year fitness resolutions. Many of us start off with strong resolve, but quickly get sidetracked by everyday life. Breaking down the KPI rollout process into basic steps can help you stay on track and stop you being overwhelmed.
Taking this further...
How to define KPIs for large or complex organisations

ROKS Enterprise: for large, complex or mission-based organisations. This approach is based on KPI Trees, an incredibly powerful and flexible, visual KPI selection method. This is the right choice for organisations that can dedicates time and resource to KPI design and definition.
Show me the ROKS Enterprise method!
What is the ROKS method?
Building KPIs is hard and has lots of hidden traps. That's why we developed a bullet-proof seven-step method for larger organisations to develop the right selection of KPIs to achieve their business goals. This method is called the ROKS Enterprise™ approach. ROKS stands for Results-Orientated KPI System. This site is packed with free resources on the ROKS Enterprise™ method and this page is designed to help you navigate the resources in a logical way, bookmark it now!
The content links are grouped by ROKS approach step. Here you go, and don't be shy about getting in touch using the contact form...
Who is the ROKS Enterprise™ approach designed for?
Medium to large enterprises that want to use their strategic objectives to develop a focussed, effective set of performance indicators. It can also be useful for smaller organisations with complex or unusual needs.
ROKS Enterprise KPI definition process overview

ROKS Enterprise: Each step in detail
Step 1: Clear Strategy
Not having a clear business strategy (or worse still, having a strategy that is woolly or vague) will completely undermine all your work on KPIs. The good news is that there are some checks you can run to see if your strategy is fit for creating meaningful KPIs.
Agree what you are trying to achieve
- Review strategy documentation
- Identify strategic objectives
- Where and how will your KPIs be used?
Step 2: Engage
Experience taught me the hard way, if you don't have the right people in the room when you develop and agree your KPIs, you might as well have not bothered - you will have to do it all over again. This step is all about identifying the right people to involve at the start, how to involve them and keeping track of that involvement.
Engage stakeholders and assess situation
- Identify key stakeholders
- Develop communications plan
- Cognitive design training
- Review existing reports and dashboards
Step 3: Longlist your KPIs with KPI Trees
People tend to want jump straight to the 'right answer' and may miss many critical KPIs by doing this. The ROKS method separates KPI selection into two stages. The first stage 'longlisting', using KPI Trees, builds a full model of all the potential KPIs, without worrying about how important or practical those measures are. This list will be waaaay too long, but don't worry, we have a structured way of reducing this list in Step 4.
KPI Trees to create 'longlist'
- Draft 'KPI Trees' in stakeholder workshops
- Run follow-up results mapping workshop
- Redraft, review and sign off KPI Trees
It's really easy to get 'carried away' and to try to measure too many things. This shortlisting step offers a bullet-proof way to reduce that list to a manageable size. It also documents the 'why' for which KPIs we selected and which we chose to leave or implement at a later stage.
Develop the measures 'shortlist'
- Workshop importance/ease-of-capture matrix
- Agree 'use, aspire or discard' list
- Set up new measures
- Develop action plans for 'use' and 'aspire' lists
Step 5: Define
Definition is all about writing down some vital information about your shortlisted KPIs, such as which data is used, precise calculations, what is or is not in included in the data etc. Honestly, most organisations will do almost anything to avoid doing this step. If you skip the KPI definition step bad things will happen. The tools provided here will help you think about, and record, all the important aspects of defining your shortlisted KPIs in a clear, logical and readable way.
Define KPIs
- Precisely define measures and KPIs
- Document known issues
- Make definitions and notes freely available
Step 6: Prototype
Fully working dashboards and reports can take lots of time, money and effort to implement. Managers often change their minds when they see new reports or dashboards, upsetting their analysts and wasting huge amounts of time and effort. You can avoid this trap by creating 'mockups' your reports, getting sign-off on fully reviewed prototypes and then building the working versions.
Design and test your dashboards and reports
- Review the prototype proposals
- Run dashboard live prototyping sessions
- Review and revise draft dashboard/report
- Approval
Step 7: Go Live
The best designed KPIs and reports are meaningless until they are part of every-day life in their organisation. Rolling out KPIs involves fixing lots of problems and people. Fortunately many of the issues have been solved in other organisations before, and many of those tools and strategies are outlined in this step. Typical challenges involve slow KPI production process, reporting tool selection, lack of trust in data quality, sustainability and many other factors.
Roll out your KPIs, reports and dashboards
- Get buy-in
- Deal with issues with existing data
- Map the KPI process
- Seek user feedback and tweaks during nursery period
- Hand over to 'business as usual' team
Rollout engagement
Dealing with problems
Tools and techniques
More useful material
Find out more
The original guide to the ROKS Enterprise method is KPI Checklists. It's available in paperback, Kindle and ePub format from Amazon and most major online book sellers.
Whilst most of the ideas you need to succeed are in the books Bernie has written, sometimes you just need some practical advice on how to apply those ideas to your organisation. A little help can give you a big boost towards your performance goals. Bernie can provide an array of KPI and improvement services to give you fresh insight and new angles to tackle your measurement and improvement problems. A quotation and situation analysis are provided in the 'Initial Review', a completely frank 60 minute phone consultation.
Here's how we do it...
Preparation: We will send you an application form, with costs and payment details for the session. Once payment is made, we will send you a preparation form by email. You can also share any materials or documents you feel will be helpful during the discussion (secure share details are included in the application form).
Timing: We will advise you of the next available consultation slot.
Qualification: Bernie has a lot of demands on his time, with only a few consulting clients accepted. If your need is outside of Bernie's' core expertise he will (gratefully) decline your application but recommend other resources to you.
Focus: These sessions are 100% focussed on delivering the best possible solution to your challenges. There's no agenda to sell further products or services to you, just the intention to deliver the best possible value.
Recording: The call will be recorded and shared with you afterwards, so there's no need to take notes and no chance of missing anything.
Satisfaction: If, within the first 15 minutes of the call, you decide that this isn't right for you, you are free to call a stop to the call - the consultation is free. After 15 mins you are committed to the whole call.
To request an application form and pricing please fill in this enquiry form...






![Complete Guide to the OKR Framework: How to Create OKRs for Your Team [2024] okr kpis and targets logo](https://madetomeasurekpis.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/okr-kpis-and-targets-logo@2x-150x150.png)
